WebClient的基本使用
简介
在 Spring 5 之前,如果我们想要调用其他系统提供的HTTP服务,我们通常可以使用 Spring 提供的 RestTemplate 来访问。RestTemplate 用法很简单,但它的不足之处在于它的请求是 同步阻塞 模式,因此存在一定的性能瓶颈,当然如果想要使用异步方式请求,也可以使用 AsyncRestTemplate。
从 Spring 5 开始,Spring 中全面引入了 Reactive 响应式编程,WebClient 就属于 Spring WebFlux 的一部分。WebClient 的请求模式属于异步非阻塞、反应式的,能够以少量固定的线程处理高并发的 HTTP 请求。
因此,从 Spring 5 开始,HTTP 服务之间的通信方式我们可以考虑使用 WebCLient 来取代之前的 RestTemplate。
重点:即使升级了 spring web 6.0.0 版本,也无法在 HttpRequestFactory 中设置请求超时,这是放弃使用 RestTemplate 的最大因素之一。
特点
webClient 是一个功能完善的 HTTP 请求客户端,支持以下内容:
- 非阻塞I/O:WebClient 构建在 Reactor 之上,它提供了一种非阻塞、反应式的方法来处理 I/O。这可以在高流量应用程序中实现更好的可扩展性和更高的性能。
- 反应流回压(即消费者负载过高时,主动反馈生产者放慢速度的机制)
- 具有高并发性,硬件资源消耗更少
- 流程的 API 设计:可以更轻松地配置和自定义请求
- 同步与异步交互
- 流式传输支持:WebClient 支持请求和响应正文的流式传输,这对于处理大文件或实时数据非常有用。
- 改进的错误处理 :WebClient 提供比 RestTemplate 更好的错误处理和日志记录,从而更轻松地诊断和解决问题。
使用方法
添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webflux</artifactId>
</dependency>创建 WebClient 实例
创建 WebClient 最简单的方法是通过静态工厂方法创建:
// 1.创建WebClient
WebClient.create();
// 2.创建WebClient并且指定baseURL
WebClient.create(String baseUrl);也可以使用 WebClient.builder 提供更多的选项:
// 3.通过builder创建WebClient
WebClient.builder().build();配置 WebClient
WebClient 实例构造器可以设置一些基础的全局web请求配置信息,比如默认的 cookie、header、baseUrl 等。
示例:
import org.springframework.http.HttpHeaders;
import org.springframework.http.HttpMethod;
import org.springframework.web.reactive.function.client.ClientResponse;
import org.springframework.web.reactive.function.client.ExchangeFilterFunction;
import org.springframework.web.reactive.function.client.WebClient;
import org.springframework.web.util.DefaultUriBuilderFactory;
import java.util.List;
public class WebClientExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
WebClient webClient = WebClient.builder()
//修改maxInMemorySize的缓存值,默认是256k,修改为10MB
.codecs(configurer->configurer.defaultCodecs().maxInMemorySize(10 * 1024 * 1024))
.clientConnector(new CustomClientHttpConnector())
.defaultCookie("sessionId", "123456")
.defaultHeaders(headers -> {
headers.add("Authorization", "Bearer token");
})
.defaultRequest(defaultRequest -> {
defaultRequest.method(HttpMethod.GET);
defaultRequest.uri("/api");
defaultRequest.headers(httpHeaders -> {
httpHeaders.add("Custom-Header", "Custom-Value");
});
})
.exchangeStrategies(builder -> {
// 配置交换策略
})
.filter(ExchangeFilterFunction.ofRequestProcessor(clientRequest -> {
// 对请求进行预处理
System.out.println("Processing request: " + clientRequest.method() + " " + clientRequest.url());
return clientRequest;
}))
.filters(filters -> {
// 添加多个自定义过滤器
filters.add(0, new CustomExchangeFilter());
})
.uriBuilderFactory(new DefaultUriBuilderFactory("https://api.example.com"))
.build();
// 发起GET请求
webClient.get()
.uri("/resource")
.retrieve()
.bodyToMono(String.class)
.doOnTerminate(() -> System.out.println("Request completed."))
.subscribe(responseBody -> System.out.println("Response body: " + responseBody));
}
// 自定义ClientHttpConnector
static class CustomClientHttpConnector implements org.springframework.web.reactive.function.client.ClientHttpConnector {
// 实现自定义的ClientHttpConnector
}
// 自定义ExchangeFilterFunction
static class CustomExchangeFilter implements ExchangeFilterFunction {
@Override
public WebClient.ResponseSpec filter(ClientRequest request, ExchangeFunction next) {
// 对请求和响应进行处理
System.out.println("Custom filter processing request: " + request.method() + " " + request.url());
return next.exchange(request);
}
}
}配置说明:
codecs(Consumer<ClientCodecConfigurer> consumer):该方法允许你配置用于请求和响应体编码和解码的编解码器,默认256KclientConnector(ClientHttpConnector connector):设置自定义的ClientHttpConnector来控制WebClient与HTTP服务器之间的通信。例如,你可以配置连接池和超时时间defaultCookie(String name, String value)和defaultCookies(Consumer<MultiValueMap<String, String>>cookiesConsumer):defaultCookie方法设置一个默认的Cookie,而defaultCookies允许你设置多个CookiedefaultHeader(String name, String value)和defaultHeaders(Consumer<HttpHeaders>headersConsumer):defaultHeader方法设置一个默认的头信息,而defaultHeaders允许你设置多个头信息defaultRequest(Consumer<DefaultUriBuilderFactory>defaultRequestConsumer):该方法配置默认的请求属性。例如,你可以设置默认的HTTP方法、URI和其他请求参数。defaultUriVariables(Consumer<DefaultUriBuilderFactory>uriVariablesConsumer):该方法允许你设置默认的URI变量,这些变量可以在URI模板中作为占位符使用。exchangeStrategies(Consumer<ExchangeStrategies.Builder>exchangeStrategiesConsumer):定制WebClient使用的交换策略,比如请求和响应体的序列化和反序列化方式。filter(ClientFilter... filters)和filters(Consumer<List<ClientFilter>>filtersConsumer):允许你为WebClient添加过滤器,用于对请求和响应进行预处理或后处理,使用filters方法添加多个过滤器,也可以使用filter方法逐个添加。uriBuilderFactory(UriBuilderFactory uriBuilderFactory):允许你设置自定义的UriBuilderFactory,用于从模板字符串创建URI。
注意:一旦构建完成,WebClient 就是不可变的,但可以mutate 克隆它并构建一个修改后的副本:
WebClient client1 = WebClient.builder()
.filter(filterA).filter(filterB).build();
// 创建一个副本
WebClient client2 = client1.mutate()
.filter(filterC).filter(filterD).build();同步发送请求(就像 RestTemplate 一样)
如果你想坚持使用发送 HTTP 请求并等待响应的老方法,也可以使用 WebClient 实现如下所示的相同功能:
public String postSynchronously(String url, String requestBody) {
LOG.info("Going to hit API - URL {} Body {}", url, requestBody);
String response = "";
try {
response =
client
.method(HttpMethod.POST)
.uri(url)
.accept(MediaType.ALL)
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
.bodyValue(requestBody)
.retrieve()
.bodyToMono(String.class)
.block();
} catch (Exception ex) {
LOG.error("Error while calling API ", ex);
throw new RunTimeException("XYZ service api error: " + ex.getMessage());
} finally {
LOG.info("API Response {}", response);
}
return response;
}block() 用于同步等待响应,这可能并不适合所有情况,你可能需要考虑 subscribe() 异步使用和处理响应。
异步发送请求
有时我们不想等待响应,而是希望异步处理响应,这可以按如下方式完成:
public static Mono<String> makePostRequestAsync(String url, String postData) {
WebClient webClient = WebClient.builder().build();
return webClient.post()
.uri(url)
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_FORM_URLENCODED)
.body(BodyInserters.fromFormData("data", postData))
.retrieve()
.bodyToMono(String.class);
}要使用此函数,只需传入要向其发送 POST 请求的 URL 以及要在请求正文中以 URL 编码字符串形式发送的数据。该函数将返回来自服务器的响应,或者如果请求由于任何原因失败,则返回一条错误消息。
要使用响应,您可以订阅Mono并异步处理响应。下面是一个例子:
makePostRequestAsync( "https://example.com/api" , "param1=value1¶m2=value2" )
.subscribe(response -> {
// 处理响应
System.out.println ( response );
}, error -> {
// 处理错误
System.err.println ( error.getMessage ());
}
);subscribe() 用于异步处理响应,你可以提供两个 lambda 表达式作为 subscribe() 的参数。如果请求成功并收到响应作为参数,则执行第一个 lambda 表达式;如果请求失败并收到错误作为参数,则执行第二个 lambda 表达式。
处理 4XX 和 5XX 错误
public static Mono<String> makePostRequestAsync(String url, String postData) {
WebClient webClient = WebClient.builder()
.baseUrl(url)
.build();
return webClient.post()
.uri("/")
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_FORM_URLENCODED)
.body(BodyInserters.fromFormData("data", postData))
.retrieve()
.onStatus(HttpStatus::is4xxClientError, clientResponse -> Mono.error(new RuntimeException("Client error")))
.onStatus(HttpStatus::is5xxServerError, clientResponse -> Mono.error(new RuntimeException("Server error")))
.bodyToMono(String.class);
}在此示例中,该 onStatus() 方法被调用两次,一次针对 4xx 客户端错误,一次针对 5xx 服务器错误。onStatus() 每次调用都采用两个参数:
- aPredicate 确定错误状态代码是否与条件匹配
- aFunction 用于返回 Mono,即要传播到订阅者的错误信息。
如果状态代码与条件匹配,Mono 则会发出相应的状态代码,并且 Mono 链会因错误而终止。在此示例中,Mono 将发出一条 RuntimeException 错误消息,指示该错误是客户端错误还是服务器错误。
根据错误状态采取行动
要根据 Mono 的 subscribe() 方法中的错误采取操作,可以在 subscribe 函数中处理响应的 lambda 表达式之后添加另一个 lambda 表达。如果在处理 Monumber 的过程中出现错误,则执行第二个 lambda 表达式。
下面是如何使用 makePostRequestAsync 函数和处理 subscribe 方法中的错误的更新示例:
makePostRequestAsync("https://example.com/api", "param1=value1¶m2=value2")
.subscribe(response -> {
// handle the response
System.out.println(response);
}, error -> {
// handle the error
System.err.println("An error occurred: " + error.getMessage());
if (error instanceof WebClientResponseException) {
WebClientResponseException webClientResponseException = (WebClientResponseException) error;
int statusCode = webClientResponseException.getStatusCode().value();
String statusText = webClientResponseException.getStatusText();
System.err.println("Error status code: " + statusCode);
System.err.println("Error status text: " + statusText);
}
});subscribe() 方法中的第二个 lambda 表达式检查错误是否是 WebClientResponseException 的实例,这是 WebClient 在服务器有错误响应时抛出的特定类型的异常。如果它是 WebClientResponseException 的实例,则代码将从异常中提取状态代码和状态文本,并将它们记录到日志中。
还可以根据发生的特定错误在此 lambda 表达式中添加其他错误处理逻辑。例如,你可以重试请求、回退到默认值或以特定方式记录错误。
处理成功响应和错误的完整代码
responseMono.subscribe(
response -> {
// handle the response
LOG.info("SUCCESS API Response {}", response);
},
error -> {
// handle the error
LOG.error("An error occurred: {}", error.getMessage());
LOG.error("error class: {}", error.getClass());
// Errors / Exceptions from Server
if (error instanceof WebClientResponseException) {
WebClientResponseException webClientResponseException =
(WebClientResponseException) error;
int statusCode = webClientResponseException.getStatusCode().value();
String statusText = webClientResponseException.getStatusText();
LOG.info("Error status code: {}", statusCode);
LOG.info("Error status text: {}", statusText);
if (statusCode >= 400 && statusCode < 500) {
LOG.info(
"Error Response body {}", webClientResponseException.getResponseBodyAsString());
}
Throwable cause = webClientResponseException.getCause();
LOG.error("webClientResponseException");
if (null != cause) {
LOG.info("Cause {}", cause.getClass());
if (cause instanceof ReadTimeoutException) {
LOG.error("ReadTimeout Exception");
}
if (cause instanceof TimeoutException) {
LOG.error("Timeout Exception");
}
}
}
// Client errors i.e. Timeouts etc -
if (error instanceof WebClientRequestException) {
LOG.error("webClientRequestException");
WebClientRequestException webClientRequestException =
(WebClientRequestException) error;
Throwable cause = webClientRequestException.getCause();
if (null != cause) {
LOG.info("Cause {}", cause.getClass());
if (cause instanceof ReadTimeoutException) {
LOG.error("ReadTimeout Exception");
}
if (cause instanceof ConnectTimeoutException) {
LOG.error("Connect Timeout Exception");
}
}
}
});超时
我们可以在每个请求中设置超时,如下所示:
return webClient
.method(this.httpMethod)
.uri(this.uri)
.headers(httpHeaders -> httpHeaders.addAll(additionalHeaders))
.bodyValue(this.requestEntity)
.retrieve()
.bodyToMono(responseType)
.timeout(Duration.ofMillis(readTimeout)) // request timeout for this request
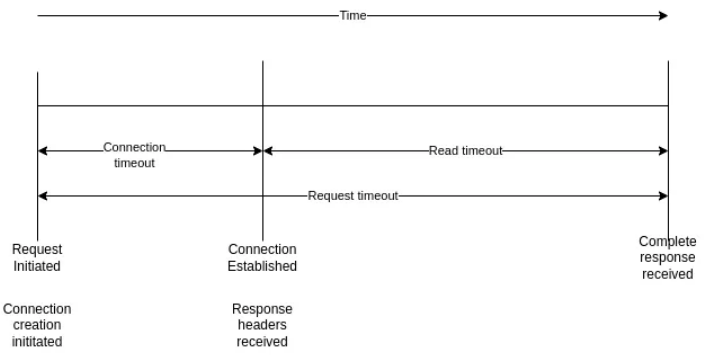
.block();但是,我们无法在每个请求中设置连接超时,这是WebClient 的属性,只能设置一次。如果需要,我们始终可以使用新的连接超时值创建一个新的 Web 客户端实例。
连接超时、读取超时和请求超时的区别如下:
示例
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*******************************设置日志打印级别*******************************/
((LoggerContext) LoggerFactory.getILoggerFactory())
.getLoggerList()
.forEach(logger -> logger.setLevel(Level.ERROR));
/******************1.设置连接超时时间********************/
/******************2.设置响应超时时间********************/
/******************3.设置读取超时时间********************/
HttpClient httpClient = HttpClient.create()
.option(ChannelOption.CONNECT_TIMEOUT_MILLIS, 5000)
.responseTimeout(Duration.ofMillis(5000))
.doOnConnected(conn -> conn.addHandlerLast(new ReadTimeoutHandler(5000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS)));
WebClient client = WebClient.builder().clientConnector(new ReactorClientHttpConnector(httpClient)).build();
String url = "http://localhost:8888/scp/mgmt/opn/log/list";
String requestBody = "{\"stime\":\"2023-07-21 10:19:00\",\"etime\":\"2023-10-19 11:19:00\",\"page\":\"1\",\"limit\":\"2\"}";
/*******************************同 步*******************************/
String response = client.method(HttpMethod.POST)
.uri(url)
// 添加请求头信息
.headers(new Consumer<HttpHeaders>() {
@Override
public void accept(HttpHeaders headers) {
headers.add("usid","a29320c00e3246bb9c76add28745c3af");
}
})
// 设置接受的媒体类型为所有类型
.accept(MediaType.ALL)
// 设置请求的内容类型为JSON
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
// 设置请求体的值,即要发送的数据
.bodyValue(requestBody)
// 执行请求并获取响应
.retrieve()
// 将响应体转换为字符串类型的Mono对象
.bodyToMono(String.class)
// 设置请求超时
.timeout(Duration.ofMillis(10000))
// 阻塞当前线程,等待响应结果并返回
.block();
System.out.println("同步响应返回:"+response);
/*******************************异 步*******************************/
Mono<String> mono = client.method(HttpMethod.POST)
.uri(url)
// 添加请求头信息
.headers(headers -> headers.add("usid", "a29320c00e3246bb9c76add28745c3af"))
// 设置接受的媒体类型为所有类型
.accept(MediaType.ALL)
// 设置请求的内容类型为JSON
.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON)
// 设置请求体的值,即要发送的数据
.bodyValue(requestBody)
// 执行请求并获取响应
.retrieve()
// 将响应体转换为字符串类型的Mono对象
.bodyToMono(String.class);
mono.subscribe(res -> System.out.println("异步响应正常返回:"+res), err -> System.out.println("异步响应异常返回:"+err.getMessage()));
// 在异步请求完成前等待一段时间(这里用于演示,在实际应用中可能不需要)
try {
Thread.sleep(5000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}工具类
ProxyDO(代理实体)
如果要使用代理,则先构建这个代理实体
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import javax.validation.constraints.NotBlank;
/**
* ProxyDO
*
* @author 陈伟伟 John Chen cww23218@ly.com
* @since 2019/11/15
*/
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
public class ProxyDO {
/**
* 服务地址(用于代理服务的地址)(必填)
*/
@NotBlank
private String serviceAddress;
/**
* 端口(必填)
*/
@NotBlank
private Integer port;
/**
* 内网IP(选填,通常用于IP切换等Job中)
*/
private String innerIp;
/**
* 用户名(选填,如有)
*/
private String userName;
/**
* 密码(选填,如有)
*/
private String password;
/**
* 获取连接字符串
* 格式:[serviceAddress]:[port]{:[userName]:[password]}
*
* @return 返回用于代理连接的字符串
*/
public String getProxyContentStr() {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder(serviceAddress + ":" + port);
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(userName)) {
stringBuilder.append(":").append(userName);
if (!StringUtils.isEmpty(password)) {
stringBuilder.append(":").append(password);
}
}
return stringBuilder.toString();
}
}WebClientUtils(主类)
public class WebClientUtils {
/**
* 默认10s超时时间
*/
private final static Duration DEFAULT_REQUEST_TIMEOUT = Duration.ofSeconds(10);
/**
* 默认代理超时时间
*/
private final static Long DEFAULT_PROXY_TIMEOUT_MILLIS = DEFAULT_REQUEST_TIMEOUT.toMillis();
//region 生成WebClient.Builder的方法
/**
* 给了一个默认的WebClient,这个Client里面配置了默认请求超时时间
*
* @return 返回一个带超时时间的{@link WebClient.Builder}
*/
public static WebClient.Builder getDefaultWebClientBuilder() {
return getWebClientBuilder(DEFAULT_REQUEST_TIMEOUT);
}
/**
* [基础创建方法]
* 给了一个默认的WebClient,这个Client里面配置了指定了请求超时时间
*
* @param requestTimeOut 请求超时时间
* @return 返回一个带超时时间的{@link WebClient.Builder}
*/
public static WebClient.Builder getWebClientBuilder(Duration requestTimeOut) {
if (requestTimeOut == null) {
requestTimeOut = DEFAULT_REQUEST_TIMEOUT;
}
return WebClient.builder().clientConnector(new ReactorClientHttpConnector(HttpClient
.create()
//重新定向开启
.followRedirect(true)
.responseTimeout(requestTimeOut)));
}
/**
* 给到一个带默认超时时间,并带有不校验任何SSL整数的WebClient
*
* @return 返回一个带默认超时时间和默认全局信任的SSL请求校验器{@link WebClient.Builder}
*/
public static WebClient.Builder getWebClientBuilderWithSslTrust() {
return getWebClientBuilderWithSslTrust(DEFAULT_REQUEST_TIMEOUT);
}
/**
* 给到一个带超时时间,并带有不校验任何SSL整数的WebClient
*
* @param requestTimeOut 超时时间
* @return 返回一个带超时时间和默认全局信任的SSL请求校验器{@link WebClient.Builder}
*/
public static WebClient.Builder getWebClientBuilderWithSslTrust(Duration requestTimeOut) {
return getWebClientBuilderWithSslTrust(requestTimeOut, false);
}
/**
* [基础创建方法]
* 给到一个带超时时间,并带有不校验任何SSL整数的WebClient
*
* @param requestTimeOut 超时时间
* @param compressionEnabled 开启压缩?默认关闭
* @return 返回一个带超时时间和默认全局信任的SSL请求校验器{@link WebClient.Builder}
*/
public static WebClient.Builder getWebClientBuilderWithSslTrust(Duration requestTimeOut, boolean compressionEnabled) {
if (requestTimeOut == null) {
requestTimeOut = DEFAULT_REQUEST_TIMEOUT;
}
return WebClient.builder().clientConnector(new ReactorClientHttpConnector(HttpClient
.create()
//重新定向开启
.followRedirect(true)
//这里注入了一个抛弃一切SSL认证的sslContext
.secure(sslContextSpec -> sslContextSpec.sslContext(SslContextBuilder.forClient().trustManager(InsecureTrustManagerFactory.INSTANCE)))
.responseTimeout(requestTimeOut)
.compress(compressionEnabled)
));
}
/**
* 给到一个带超时时间,带代理,并带有不校验任何SSL整数的WebClient
*
* @param requestTimeOut 超时时间
* @param proxyDO 代理实体
* @return 返回一个带超时时间和默认全局信任的SSL请求校验器{@link WebClient.Builder}
*/
public static WebClient.Builder getWebClientBuilderWithSslTrustAndPolicy(Duration requestTimeOut, ProxyDO proxyDO) {
return getWebClientBuilderWithSslTrustAndPolicy(requestTimeOut, proxyDO, false);
}
/**
* [基础创建方法]
* 给到一个带超时时间,带代理,并带有不校验任何SSL整数的WebClient
*
* @param requestTimeOut 超时时间
* @param proxyDO 代理实体
* @param compressionEnabled 开启压缩?默认关闭
* @return 返回一个带超时时间和默认全局信任的SSL请求校验器{@link WebClient.Builder}
*/
public static WebClient.Builder getWebClientBuilderWithSslTrustAndPolicy(Duration requestTimeOut, ProxyDO proxyDO, boolean compressionEnabled) {
if (requestTimeOut == null) {
requestTimeOut = DEFAULT_REQUEST_TIMEOUT;
}
return WebClient.builder().clientConnector(new ReactorClientHttpConnector(HttpClient
.create()
//这里注入了一个抛弃一切SSL认证的sslContext
.secure(sslContextSpec -> sslContextSpec.sslContext(SslContextBuilder.forClient().trustManager(InsecureTrustManagerFactory.INSTANCE)))
.responseTimeout(requestTimeOut)
.compress(compressionEnabled)
//重新定向开启
.followRedirect(true)
//Spring Boot 2.4 以上
.proxy(proxy -> proxy
.type(ProxyProvider.Proxy.HTTP)
.host(proxyDO.getServiceAddress())
.port(proxyDO.getPort())
.username(proxyDO.getUserName())
.password(username -> proxyDO.getPassword()))
//
// .tcpConfiguration(tcpClient -> tcpClient.proxy(
// p -> {
// ProxyProvider.Builder pb = p.type(ProxyProvider.Proxy.HTTP)
// .address(InetSocketAddress.createUnresolved(proxyDO.getServiceAddress(), proxyDO.getPort()));
// if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(proxyDO.getUserName())) {
// pb.username(proxyDO.getUserName())
// .password(v -> proxyDO.getPassword());
// }
// Long proxyTimeOutMillis = proxyDO.getProxyTimeOutMillis();
// if (proxyTimeOutMillis != null && proxyTimeOutMillis > 0) {
// pb.connectTimeoutMillis(proxyTimeOutMillis);
// } else {
// pb.connectTimeoutMillis(DEFAULT_PROXY_TIMEOUT_MILLIS);
// }
// }
// ))
));
}
/**
* 将http相应中的Cookie转换为用于http请求中的cookie
* 方法中仅进行简单转换,不会对Cookie有效期等进行判断
*
* @param responseCookie 需要被转换的cookie
* @return 返回可以用于请求的Cookies
*/
public static MultiValueMap<String, String> transformResponseCookiesToRequestCookies(MultiValueMap<String, ResponseCookie> responseCookie) {
MultiValueMap<String, String> ret = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
if (responseCookie == null || responseCookie.size() == 0) {
return ret;
}
for (Map.Entry<String, List<ResponseCookie>> entity : responseCookie.entrySet()) {
String key = entity.getKey();
List<ResponseCookie> value = entity.getValue();
int size = value.size();
if (size == 0) {
continue;
}
List<String> cookies = new ArrayList<>(size);
for (ResponseCookie cookie : value) {
cookies.add(cookie.getValue());
}
ret.addAll(key, cookies);
}
return ret;
}
}
