SpringBootTest详解
提起“单元测试”这几个字,一般开发者会条件反射般想起:“工作忙,没时间”,这是一个客观上的事实,在急于求成的大环境下,规范的单元测试却需要一些明确的代码产出及覆盖率指标,这的确很让人头疼。早几年的关于单元测试的文章,不停的鼓吹其好处,却对时间成本的问题视而不见。
而与此相对的,对于开发者而言,其编写的代码是否需要经过测试,经过几轮测试才能让开发者安心?相信大多数开发者会说需要,且测试次数越多越好,毕竟上线时求神拜佛的滋味其实并不好受。
所以这其实是自相矛盾的,我们身处其中,有时候只能抱测试哥哥的大腿以求生路。但是仅仅靠测试人员把关,有些细节和异常流程不可避免会被漏掉。
单元测试的缺点
回到单元测试本身的概念上来,单元测试强调剥离所有外部依赖的影响,对类中的每个方法都写一个测试 case,这里面本身存在一些现实问题:
- 为每个方法写测试 case,时间成本太高
- 有些方法的操作本身非常简单,只是一些简单的赋值等操作,没有必要写测试
- 团队开发能力参差不齐,解耦做的不好的情况下,单元测试越发困难
- 有些依赖非常难以剥离(进行 mock),或者剥离的代价比较大,比如 mvc 中 Controller 需要web容器,数据库访问需要真实数据库(使用内存数据库,初始化的工作量也非常大),Redis 等
单元测试,仅适合那些逻辑复杂,逻辑分叉较多且较少依赖外部环境的方法,这些方法使用 unit test 再合适不过。除此之外的其他业务场景,建议舍弃 单元测试,投入到“功能测试”的怀抱。
功能测试
在本文中,我们对功能测试做一下约定:在单个 Java 虚拟机内部的,mock 大部分外部依赖的影响,针对业务功能(通常是 Controller 或对外公开的 Service)的测试,称之为“功能测试”,把单个服务内部的业务功能综合在一起,每一个测试 case 都是一个小业务流程。
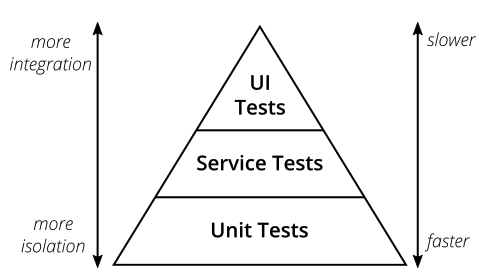
测试金字塔中的第二层是我们重点关注的,unit test 虽好,但常规的业务开发中用的不多。
功能测试不同于集成测试(UI 测试),集成测试原意是强调端到端的完整链路测试,期望环境尽可能是真实的,每一个测试 case 都是一个完整的业务流程,本文不讨论集成测试相关内容。
用测试代码安安心心的写出一条功能测试 case,确保它能够正确执行,每个核心业务功能一条测试 case。这样仍需做一些 mock 工作,但 mock 工作量变小了很多,再加上 Spring 框架支持,进一步减轻了测试工作量。
Spring Boot Test 简介
Spring Test 与 JUnit 等其他测试框架结合起来,提供了便捷高效的测试手段。而 Spring Boot Test 是在 Spring Test 之上的再次封装,增加了 切片测试,增强了mock 能力。
整体上,Spring Boot Test 支持的测试种类,大致可以分为如下三类:
| 类别 | 描述 | 涉及的注解 |
|---|---|---|
| 单元测试 | 一般面向方法,编写一般业务代码时,测试成本较大(理由见上文) | @Test |
| 切片测试 | 一般面向难于测试的边界功能,介于单元测试和功能测试之间 | @RunWith、@WebMvcTest 等 |
| 功能测试 | 一般面向某个完整的业务功能,同时也可以使用切面测试中的mock能力,推荐使用 | @RunWith、@SpringBootTest 等 |
功能测试 过程中的几个关键要素及支撑方式如下:
| 要素 | 实现方式 |
|---|---|
| 测试运行环境 | 通过 @RunWith 和 @SpringBootTest 启动 spring 容器 |
| mock能力 | Mockito 提供了强大 mock 功能 |
| 断言能力 | AssertJ、Hamcrest、JsonPath 提供了强大的断言能力 |
快速开始
增加 spring-boot-starter-test 依赖,使用 @RunWith和 @SpringBootTest 注解,即可开始测试。
添加依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>一旦依赖了 spring-boot-starter-test,下面这些类库将被一同依赖进去:
| 名称 | 简介 |
|---|---|
| JUnit | Java 测试事实上的标准,默认依赖版本是4.12(JUnit5 和 JUnit4 差别比较大,集成方式有不同) |
| Spring Test & Spring Boot Test | Spring 的测试支持 |
| AssertJ | 提供了流式的断言方式 |
| Hamcrest | 提供了丰富的 matcher |
| Mockito | mock 框架,可以按类型创建 mock 对象,可以根据方法参数指定特定的响应,也支持对于 mock 调用过程的断言 |
| JSONassert | 为 JSON 提供了断言功能 |
| JsonPath | 为 JSON 提供了 XPATH 功能 |
测试类
package com.example.learn.springboottestlearn.ttt;
import com.example.learn.springboottestlearn.entity.User;
import com.example.learn.springboottestlearn.service.UserService;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class SpringBootTestLearnApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
@Test
public void testAddUser() {
User user = new User();
user.setName("john");
user.setAddress("earth");
userService.add(user);
}
}@RunWith 是 Junit4 提供的注解,将 Spring 和 Junit 链接了起来。
假如使用Junit5,不再需要使用 @ExtendWith 注解,@SpringBootTest 和其它 @*Test 默认已经包含了该注解。
@SpringBootTest 替代了 spring-test 中的 @ContextConfiguration 注解,目的是加载 ApplicationContext,启动 spring 容器。
使用 @SpringBootTest 时并没有像 @ContextConfiguration 一样显示指定 locations 或 classes 属性,原因在于 @SpringBootTest 注解会自动检索程序的配置文件,检索顺序是从当前包开始,逐级向上查找被 @SpringBootApplication 或 @SpringBootConfiguration 注解的类。
回忆一下 Spring 整合 JUnit 的步骤:

功能测试
一般情况下,使用 @SpringBootTest 后,Spring 将 加载所有被管理的 bean,基本等同于启动了整个服务,此时便可以开始功能测试。
由于 web 服务是最常见的服务,且我们对于 web 服务的测试有一些特殊的期望,所以 @SpringBootTest 注解中,给出了 webEnvironment 参数指定了 web 的environment,该参数的值一共有四个可选值:
| 名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| MOCK | 此值为默认值,该类型提供一个 mock 环境,可以和 @AutoConfigureMockMvc 或 @AutoConfigureWebTestClient 搭配使用,开启Mock 相关的功能。注意此时内嵌的服务(servlet 容器)并没有真正启动,也不会监听 web 服务端口。 |
| RANDOM_PORT | 启动一个真实的 web 服务,监听一个随机端口。 |
| DEFINED_PORT | 启动一个真实的 web 服务,监听一个定义好的端口(从 application.properties 读取)。 |
| NONE | 启动一个非 web 的 ApplicationContext,既不提供 mock 环境,也不提供真实的 web 服务。 |
另外,如果当前服务的 classpath 中没有包含web相关的依赖,spring 将启动一个非 web 的 ApplicationContext,此时的 webEnvironment 就没有什么意义了
切片测试
所谓切片测试,官网文档称为 “slice” of your application,实际上是对一些特定组件的称呼。这里的 slice 并非单独的类(毕竟普通类只需要基于JUnit的单元测试即可),而是介于单元测试和集成测试中间的范围。
slice 是指一些在特定环境下才能执行的模块,比如 MVC 中的 Controller、JDBC 数据库访问、Redis 客户端等,这些模块大多脱离特定环境后不能独立运行,假如spring 没有为此提供测试支持,开发者只能启动完整服务对这些模块进行测试,这在一些复杂的系统中非常不方便,所以 spring 为这些模块提供了测试支持,使开发者有能力单独对这些模块进行测试。
通过 @*Test 开启具体模块的测试支持,开启后 spring 仅加载相关的 bean,无关内容不会被加载。
使用 @WebMvcTest 用来校验 controllers 是否正常工作的示例:
import org.junit.*;
import org.junit.runner.*;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.web.servlet.*;
import org.springframework.boot.test.mock.mockito.*;
import static org.assertj.core.api.Assertions.*;
import static org.mockito.BDDMockito.*;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.request.MockMvcRequestBuilders.*;
import static org.springframework.test.web.servlet.result.MockMvcResultMatchers.*;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@WebMvcTest(UserVehicleController.class)
public class MyControllerTests {
@Autowired
private MockMvc mvc;
@MockBean
private UserVehicleService userVehicleService;
@Test
public void testExample() throws Exception {
given(this.userVehicleService.getVehicleDetails("sboot"))
.willReturn(new VehicleDetails("Honda", "Civic"));
this.mvc.perform(get("/sboot/vehicle").accept(MediaType.TEXT_PLAIN))
.andExpect(status().isOk()).andExpect(content().string("Honda Civic"));
}
}使用 @WebMvcTest 和 MockMvc 搭配使用,可以在不启动 web 容器的情况下,对 Controller 进行测试。
小结
上文文主要介绍了如下几点内容:
- 测试可以分为 单元测试、功能测试、以及介于两者之间的 切片测试
- 建议放弃不必要的单元测试,拥抱功能测试、切片测试。
- Spring Boot Test 在 spring-test 基础上,增强了mock能力,增加了测试的自动配置、切片测试。
@SpringBootTest、@WebMvcTest等其他@*Test注解, 作为开启测试的注解,都可以启动一个 ApplicationContext。
Spring 为了避免的繁琐难懂的xml配置,引入大量 annotation 进行系统配置,确实减轻了配置工作量。由此,理解这些 annotation 变得尤为重要,一定程度上讲,对 Spring Boot Test 的使用,就是对其相关 annotation 的使用。
掌握这些 annotation(及部分关联的类),可以从注解功能分类,相互之间的搭配组合,及相似注解的差异这三方面着手。
按功能分类
本文仅讨论Spring Boot Test(版本:2.1.1.BUILD-SNAPSHOT)中的注解。
由于使用这些注解的使用方式大多比较简单,为避免干扰阅读,本文不再罗列代码示例。
从功能上讲,Spring Boot Test 中的注解主要分如下几类:
| 类别 | 示例 | 格式 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 配置类型 | @TestConfiguration等 | 提供一些测试相关的配置入口 | |
| mock 类型 | @MockBean等 | 提供 mock 支持 | |
| 启动测试类型 | @SpringBootTest | @\*Test | 以 Test 结尾的注解,具有加载 applicationContext 的能力 |
| 自动配置类型 | @AutoConfigureJdbc等 | @AutoConfigure* | 以 AutoConfigure 开头的注解,具有加载测试支持功能的能力。 |
配置类型的注解
| 注解 | 作用 | 实践中的使用 |
|---|---|---|
@TestComponent | 该注解另一种@Component,在语义上用来指定某个Bean是专门用于测试的。 | 该注解适用于测试代码和正式混合在一起时,不加载被该注解描述的Bean,使用不多。 |
@TestConfiguration | 该注解是另一种@TestComponent,它用于补充额外的Bean或覆盖已存在的Bean | 在不修改正式代码的前提下,使配置更加灵活 |
@TypeExcludeFilters | 用来排除@TestConfiguration和@TestComponent | 适用于测试代码和正式代码混合的场景,使用不多 |
@OverrideAutoConfiguration | 可用于覆盖@EnableAutoConfiguration,与ImportAutoConfiguration结合使用,以限制所加载的自动配置类 | 在不修改正式代码的前提下,提供了修改配置自动配置类的能力 |
@PropertyMapping | 定义@AutoConfigure*注解中用到的变量名称,例如在@AutoConfigureMockMvc中定义名为spring.test.mockmvc.webclient.enabled的变量 | 一般不使用 |
使用
@SpringBootApplication启动测试或者生产代码,被@TestComponent描述的Bean会自动被排除掉。如果不是则需要向@SpringBootApplication添加TypeExcludeFilter。
mock 类型的注解
| 注解 | 作用 |
|---|---|
@MockBean | 用于mock指定的class或被注解的属性 |
@MockBeans | 使@MockBean支持在同一类型或属性上多次出现 |
@SpyBean | 用于spy指定的class或被注解的属性 |
@SpyBeans | 使@SpyBeans支持在同一类型或属性上多次出现 |
@MockBean 和 @SpyBean 这两个注解,在 mockito 框架中本来已经存在,且功能基本相同。Spring Boot Test又定义一份重复的注解,目的在于使MockBean和 SpyBean 被ApplicationContext管理,从而方便使用。
MockBean和SpyBean功能非常相似,都能模拟方法的各种行为。不同之处在于MockBean是全新的对象,跟正式对象没有关系;而SpyBean与正式对象紧密联系,可以模拟正式对象的部分方法,没有被模拟的方法仍然可以运行正式代码。
自动配置类型的注解(@AutoConfigure*)
| 注解 | 作用 |
|---|---|
@AutoConfigureJdbc | 自动配置JDBC |
@AutoConfigureCache | 自动配置缓存 |
@AutoConfigureDataLdap | 自动配置LDAP |
@AutoConfigureJson | 自动配置JSON |
@AutoConfigureJsonTesters | 自动配置JsonTester |
@AutoConfigureDataJpa | 自动配置JPA |
@AutoConfigureTestEntityManager | 自动配置TestEntityManager |
@AutoConfigureRestDocs | 自动配置Rest Docs |
@AutoConfigureMockRestServiceServer | 自动配置 MockRestServiceServer |
@AutoConfigureWebClient | 自动配置 WebClient |
@AutoConfigureWebFlux | 自动配置 WebFlux |
@AutoConfigureWebTestClient | 自动配置 WebTestClient |
@AutoConfigureMockMvc | 自动配置 MockMvc |
@AutoConfigureWebMvc | 自动配置WebMvc |
@AutoConfigureDataNeo4j | 自动配置 Neo4j |
@AutoConfigureDataRedis | 自动配置 Redis |
@AutoConfigureJooq | 自动配置 Jooq |
@AutoConfigureTestDatabase | 自动配置Test Database,可以使用内存数据库 |
这些注解可以搭配 @\*Test 使用,用于开启在 @\*Test 中未自动配置的功能。例如 @SpringBootTest 和 @AutoConfigureMockMvc 组合后,就可以注入org.springframework.test.web.servlet.MockMvc。
“自动配置类型”有两种使用方式:
- 在功能测试(即使用
@SpringBootTest)时显示添加。- 一般在切片测试中被隐式使用,例如
@WebMvcTest注解时,隐式添加了@AutoConfigureCache、@AutoConfigureWebMvc、@AutoConfigureMockMvc。
实现原理 与
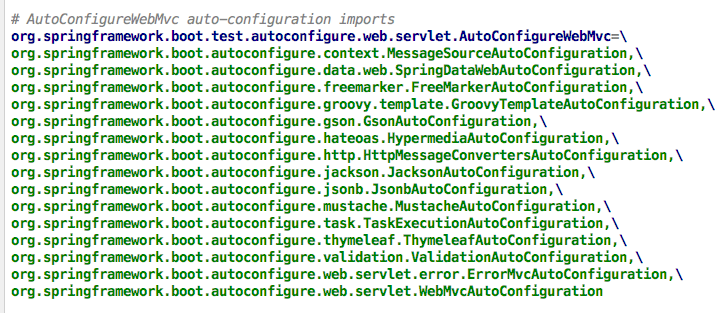
spring-boot-autoconfigure中的@\*AutoConfiguration实现略有不同,Test包中的@AutoConfigure\*通过DeterminableImports接口作为指定代码的识别入口,通过ImportAutoConfiguration注解作为配置入口,从Test包下的spring.factories读取配置文件,每个@AutoConfigure\*中都可以包含多个 Spring Boot 的@\*AutoConfiguration,例如:
启动测试类型的注解(@*Test)
所有的 @\*Test 注解都被 @BootstrapWith 注解,它们可以启动 ApplicationContext,是测试的入口,所有的测试类必须声明一个 @\*Test 注解。
| 注解 | 作用 | |
|---|---|---|
@SpringBootTest | 自动侦测并加载@SpringBootApplication或@SpringBootConfiguration中的配置,默认web环境为MOCK,不监听任务端口 | |
@DataRedisTest | 测试对Redis操作,自动扫描被@RedisHash描述的类,并配置Spring Data Redis的库 | |
@DataJpaTest | 测试基于JPA的数据库操作,同时提供了TestEntityManager替代JPA的EntityManager | |
@DataJdbcTest | 测试基于Spring Data JDBC的数据库操作 | |
@JsonTest | 测试JSON的序列化和反序列化 | |
@WebMvcTest | 测试Spring MVC中的controllers | |
@WebFluxTest | 测试Spring WebFlux中的controllers | |
@RestClientTest | 测试对REST客户端的操作 | |
@DataLdapTest | 测试对LDAP的操作 | |
@DataMongoTest | 测试对MongoDB的操作 | |
@DataNeo4jTest | 测试对Neo4j的操作 |
除了
@SpringBootTest之外的注解都是用来进行切面测试的,他们会默认导入一些自动配置,点击 官方docs 查看详情。
一般情况下,推荐使用@SpringBootTest而非其它切片测试的注解,简单有效。若某次改动仅涉及特定切片,可以考虑使用切片测试。
@SpringBootTest是这些注解中最常用的一个,其中包含的配置项如下:
| 配置名称 | 说明 |
|---|---|
value | 指定配置属性 |
properties | 指定配置属性,和value意义相同 |
classes | 指定配置类,等同于@ContextConfiguration中的class,若没有显示指定,将查找嵌套的@Configuration类,然后返回到SpringBootConfiguration搜索配置 |
webEnvironment | 指定web环境,可选值有:MOCK、RANDOM_PORT、DEFINED_PORT、NONE |
webEnvironment详细说明:
| 可选值 | 说明 |
|---|---|
MOCK | 此值为默认值,该类型提供一个mock环境,此时内嵌的服务(servlet容器)并没有真正启动,也不会监听web端口。 |
RANDOM_PORT | 启动一个真实的web服务,监听一个随机端口。 |
DEFINED_PORT | 启动一个真实的web服务,监听一个定义好的端口(从配置中读取)。 |
NONE | 启动一个非web的 ApplicationContext,既不提供mock环境,也不提供真是的web服务。 |
相互之间的搭配组合
典型的搭配如下:
package sample.test;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import sample.test.domain.VehicleIdentificationNumber;
import sample.test.service.VehicleDetails;
import sample.test.service.VehicleDetailsService;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.autoconfigure.jdbc.AutoConfigureTestDatabase;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest.WebEnvironment;
import org.springframework.boot.test.mock.mockito.MockBean;
import org.springframework.boot.test.web.client.TestRestTemplate;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import static org.mockito.BDDMockito.given;
/**
* {@code @SpringBootTest} with a random port for {@link SampleTestApplication}.
*
* @author Phillip Webb
*/
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)
@AutoConfigureTestDatabase
public class SampleTestApplicationWebIntegrationTests {
private static final VehicleIdentificationNumber VIN = new VehicleIdentificationNumber(
"01234567890123456");
@Autowired
private TestRestTemplate restTemplate;
@MockBean
private VehicleDetailsService vehicleDetailsService;
@Before
public void setup() {
given(this.vehicleDetailsService.getVehicleDetails(VIN))
.willReturn(new VehicleDetails("Honda", "Civic"));
}
@Test
public void test() {
this.restTemplate.getForEntity("/{username}/vehicle", String.class, "sframework");
}
}@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)是JUnit的注解,作用是关联 Spring Boot Test,使运行JUnit时同时启动Spring@SpringBootTest(webEnvironment = WebEnvironment.RANDOM_PORT)作用是启动 Spring 的 ApplicationContext,参数 webEnvironment 指定了运行的web环境@AutoConfigureTestDatabase作用是启动一个内存数据库,不使用真实的数据库
其中 @RunWith 和 @\*Test 必须存在,@AutoConfigure 可以同时配置任意多个,而配置类型的注解可以在需要时添加。
相似注解的区别和联系
@TestComment vs @Comment
@TestComponent是另一种@Component,在语义上用来指定某个Bean是专门用于测试的- 使用
@SpringBootApplication服务时,@TestComponent会被自动排除
@TestConfiguration vs @Configuration
@TestConfiguration是Spring Boot Boot Test提供的,@Configuration是Spring Framework提供的。@TestConfiguration实际上是也是一种@TestComponent,只是这个@TestComponent专门用来做配置用。@TestConfiguration和@Configuration不同,它不会阻止@SpringBootTest的查找机制,相当于是对既有配置的补充或覆盖。
@SpringBootTest vs @WebMvcTest(或@*Test)
- 都可以启动Spring的 ApplicationContext
@SpringBootTest自动侦测并加载@SpringBootApplication或@SpringBootConfiguration中的配置,@WebMvcTest不侦测配置,只是默认加载一些自动配置。@SpringBootTest测试范围一般比@WebMvcTest大。
@MockBean vs @SpyBean
详见上文 [mock类型的注解]
小结
本文主要介绍了 Spring Boot Tes t中新增的注解,笔者将这些注解分为这几个类型:配置类型、mock类型、启动测试类型、自动配置类型。
- “配置类型”中的
@TestComponent、@TestConfiguration、@OverrideAutoConfiguration使配置更加灵活。 - 封装了
mockito的@MockBean和@SpyBean,使其可以自然的注入到Spring容器中。 - 每个测试类必须包含一个“启动测试类型”的注解(
@\*Test),同时可以根据需要添加”自动配置类型”的注解(@AutoConfigure*)。 @SpringBootTest是最常用的“启动测试类型”注解